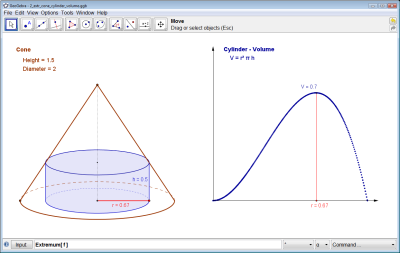
If you haven’t discovered Geogebra yet, follow this link:
21. Multiplying 6×6 to 10×10 on your fingers
This is a great video from Youtube:
20. Polygon Challenge
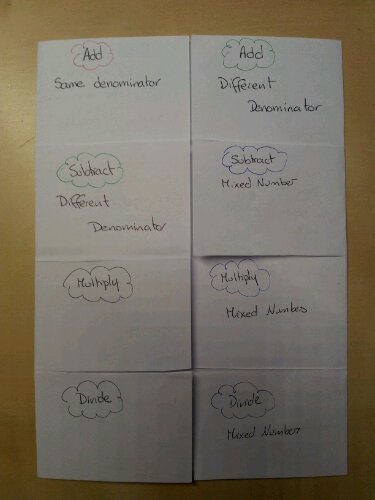
19. Fraction Skills Foldable
This resource was designed to recap basic fraction skills as part of KS4 revision. The foldable covers:
1. Addition with common denominator
2. Addition with different denominators (butterfly method)
3. Subtraction with different denominators (butterfly method)
4. Subtraction with mixed numbers
5. Multiplication
6. Multiplication with mixed numbers
7. Division (reciprocal method)
8. Division of a whole number by a fraction
It also deals with equivalent fractions, simplifying and converting between mixed & improper fractions.
Each section has a title, method and example.
This is a draft ‘teacher’ version. My students made theirs look really good with different colours, highlighter and their own examples.
Note: this isn’t for teaching a full understanding of fraction manipulation, just summarising facts.
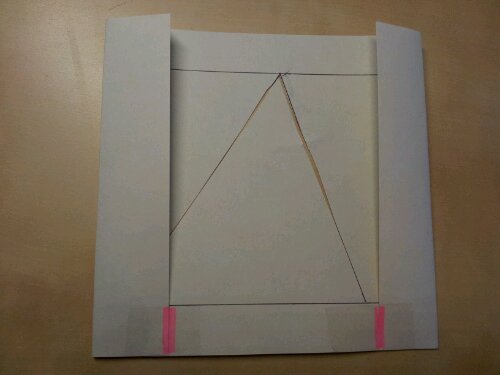
18. Similar triangles
This quick activity shows that although the sides change in similar triangles, the angles stay the same. It can also be used with enlargement.
Equipment
Two pieces of different coloured card (A5 or A6 is fine)
Ruler
Pencil
Scissors
Sticky tape
Step by step instructions
Two Lines
Draw a line parallel to the long sides of one piece of card (min 2cm from the edge)
Wrap
Place the two pieces of card at 90 degrees to make a cross.
Wrap the lined card around the unlined card
Cut
Mark out a triangle using the pencil lines as a guide.
Cut along two sides as shown. It’s okay to tidy up a messy cut, so long as the line remains straight.
Stick
Turn over the card and refold in the opposite direction. Stick the bottom edge of the folded card in place, as shown.
Slide
Slot the second piece in place.
Turn over.
As the slider moves up and down a contrasting triangle appears and disappears.
You can measure the sides & angles of every triangle you make.
This can be stuck into books by gluing along the folded edges, which still allows the slider to move.
17. Rotational symmetry rug
I love this rug for discussing rotational symmetry.
If you project the image on a whiteboard, students can draw different symmetries on it.
16. Library Fines (Sequences)
County Library
The first day a book is overdue, you are charged 4p. Each day incurs another 4p.
What are the charges for the first week?
(4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28)
What is the Nth term?
(4N)
How much would you be charged for being 25 days late?
(100p)
Village library
The village library charges 10p for the first day and 3p for every subsequent day.
What are the charges for the first week?
(10, 13, 16, 19, 22, 25, 28)
What is the Nth term?
(3N+7)
What is the charge for 30 days?
(97p)
How many days late is one book if the fine is more than £2?
(Solve 3N+7>200)
Look back at both libraries. Under what conditions do the libraries have the cheapest fines?
(1-6 days: County Library
7 days: same
8+: Village library)
Extension
Why do the libraries have the same charge on the 7th day?
Prove it algebraically.
(Solve 3N+7=4N)
You can also extend this investigation to looking at calendar dates, with one library open 5 days a week and the other being open 6 days with fines only applying when libraries are open. How would this affect the ‘cheapness’ of fines when days are included?
Adaptations
This method can be used for car hire, mobile phone comparisons, energy bills because sequences link so well with graphs of real life problems.